In this article, we are going to learn about .NET and its capabilities. We’ll see what .NET is, what different application models .NET supports, why should we use it, and some limitations.
So let’s get going.
What is .NET?
.NET is a free, cross-platform, open source developer platform, in which we can create different types of applications. Designed and developed by Microsoft, it supports the use of multiple programming languages, and code editors, and runs on multiple platforms. One of the major goals of .NET is to provide developers with a single platform for application development. These applications can be of different types and can run on different operating systems.
In a nutshell, .NET consists of the runtime environment, compilers, languages, and base class libraries. On top of that, there are several application models. Each application model caters to specific types of applications like the cloud, web, desktop, mobile, etc.
Different Implementations
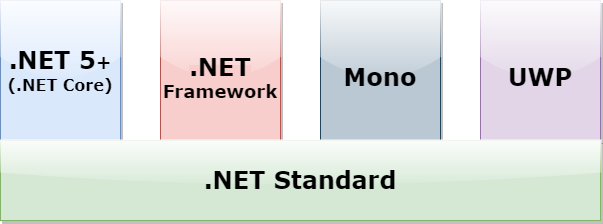
Let’s take a look at the different .NET implementations:
.NET 5+(previously .NET Core) is the cross-platform implementation of .NET that can run on Windows, macOS, and Linux. We can develop different types of applications like cloud, web, desktop, etc. using it. As of the date of writing this article, the latest version is .NET 6 but .NET 7 is in preview mode.
.NET Framework is old and original .NET implementation that is available since 2002. We can use it to develop both web and desktop applications. However, it is optimized for building desktop applications and runs only on Windows. As of the date of writing this article, the latest version is .NET Framework 4.8.1.
Mono is a .NET implementation that supports building Xamarin-based mobile applications on Android, iOS, etc.
UWP is an implementation of .NET that we can use to build touch-enabled applications for the Internet of Things(IoT). It can target different types of devices like PCs, tablets, phones, Xbox, etc.
To maintain uniformity, different .NET implementations share a common set of components and APIs. This minimal set of libraries is called the .NET Standard. The latest version is .NET standard 2.1 and Microsoft does not plan to release new versions. That said, all future versions of .NET will continue to support current and earlier versions of the .NET Standard.
To learn more about all the differences between .NET Framework, .NET Standard, and .NET Core, you can read our article on this subject.
Different Languages
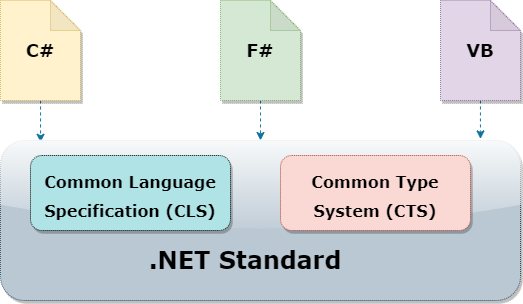
While using .NET, we can use different languages to write programs. Let’s take a look at a few popular .NET languages:
C# is a modern, object-oriented, and type-safe language. It is a good choice for developing web, desktop, and mobile apps. For learning more about C#, check out our C# Series.
F# is a general-purpose functional programming language that supports both object-oriented and imperative programming approaches. It is a good choice for developing high-performing business software, data science, and machine learning applications.
Visual Basic is an easy-to-understand language with simple syntax. It supports object-oriented concepts and makes it easy to develop type-safe .NET apps. One of the biggest advantages of Visual Basic is the support for the quick development of Windows forms and UI-based applications.
Common Type System(CTS) describes all the types that .NET languages should support and Common Language Specification(CLS) defines the set of features that all .NET languages should support. This ensures interoperability between the languages.
What Can We Do With .NET?
With .NET, we can build different types of applications like web apps, cloud apps, mobile apps, desktop apps, games, IoT apps, etc. that can target different platforms.
Let’s take a look at some of the popular app types that we can build using .NET:
- Cloud Apps –
.NETis an excellent choice for building modern cloud apps that are fast and scalable. These apps can target any cloud platform. However,.NETand Visual Studio provide several integrations with Azure services that make it easy to develop cloud-native apps. - Web Apps –
.NETis a great platform for building web apps, APIs, real-time apps, and microservices. ASP.NET extends.NETwith additional tools and libraries required to develop web apps. On top of that, we can use Blazor to build interactive web UI with C#. - Mobile Apps – .NET Multi-platform App UI (MAUI) supports building cross-platform desktop and mobile apps that can target various operating systems like iOS, Android, macOS, Windows, etc.
- Desktop Apps – For developing desktop apps, apart from the MAUI, we can use Blazor Hybrid or the Windows App SDK.
- Games – For developing games, we can use Unity, which is a real-time 3D development platform for building games and simulations.
- Machine Learning & AI – With
.NET, it is very easy to build intelligent apps that can detect emotions and sentiments, recognize speech and vision, language understanding, search capability, etc. using services like ML.NET, Cognitive Services, etc. - Internet of Things (IoT) –
.NETprovides very good support for building IoT apps for devices and sensors like the Raspberry Pi, HummingBoard, etc.
.NET Application Models
Now let’s take a look at the .NET application models in detail:
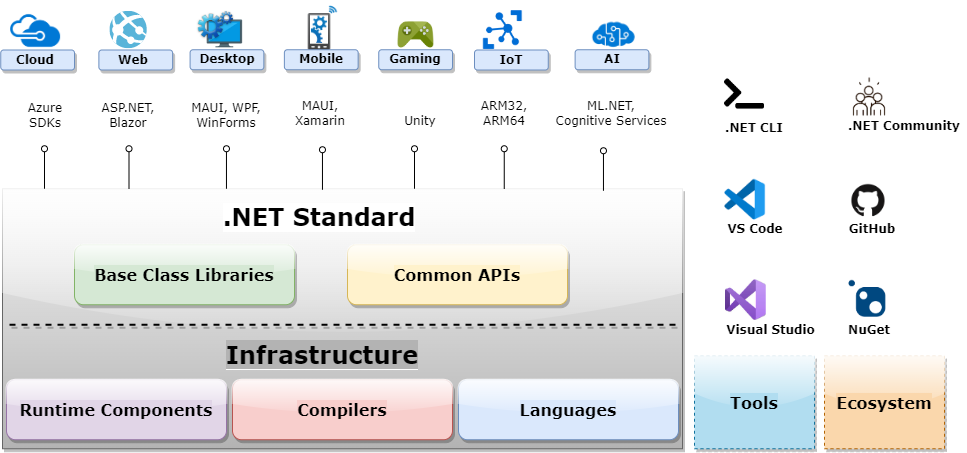
.NET consists of a set of base libraries and various application models built on top of that, which we can leverage for building different types of applications.
At the core of .NET lies the infrastructure that consists of the runtime components, compilers, and languages. The base class libraries and common APIs sit on top of that, which comprises the .NET standard. On top of that, there are several application models and load sets that are specific to various application types.
For instance, if we want to build modern, fast, and scalable cloud applications, .NET provides a rich set of Azure SDKs and APIs. If we are looking to build web apps, ASP.NET Core and Blazor are excellent choices. On the other hand, .NET MAUI is a great platform for building both desktop and mobile apps. Xamarin is a great choice for native mobile app development whereas Unity is the go-to choice for game development. Similarly, .NET provides application models for developing IoT, AI/ML apps, etc.
Development Tools
A Visual Studio is a great tool for developing and debugging .NET applications. It is a fully-featured Integrated Development Environment(IDE) and is available for Windows and Mac. The community edition of Visual Studio is free while the professional and enterprise editions require a subscription and are targeted at small development teams and big enterprises respectively.
A Visual Studio Code is a free standalone source code editor that runs on Windows, Linux, and Mac. With a large number of extensions available, it can support just about any programming language.
The .NET Command Line Interface(CLI) comes with .NET SDK and we can use it to quickly create, build and run cross-platform apps. CLI works on Windows, Linux, and Mac.
Apart from these, there are other popular third-party tools that we can use for developing .NET applications like the JetBrains Rider, OmniSharp, etc.
The .NET Ecosystem & Community
We can extend the functionality of our .NET applications by using Microsoft and third-party packages. NuGet is a very popular package manager that is built specifically for .NET.
Being open-source, the .NET foundation manages the development and collaboration around the .NET ecosystem. Furthermore, the .NET source code is available on GitHub and a large number of developers and companies contribute to it.
Apart from that, .NET has a very active developer community on most of the popular online platforms. This means we would always get good help and support from the community on development-related queries and challenges.
Why Should We Choose .NET?
Let’s discuss why we should choose .NET over other development platforms:
Productive – .NET is a highly productive platform and we can use it to create high-quality applications very quickly. Modern programming language features like asynchronous programming, generics, Language Integrated Query(LINQ), etc. makes developers more productive. Adding to it, the extensive list of libraries and APIs and best-in-class development tools like Visual Studio, VS Code, etc., make it one of the most productive development platforms.
Cross-Platform– With .NET, we can build different types of applications that target different platforms. We can use the same set of skills and tools for developing different kinds of applications on different platforms which results in quicker development times and reduced costs.
Loved by Developers – The developer community around the world loves and appreciates the .NET platform as it is modern and open-source. It is consistently ranked as one of the most loved development frameworks in various developer surveys.
High Performing – .NET applications are very fast and provide quick responses and consume fewer resources. In popular performance benchmarks, .NET consistently outperforms other web development frameworks especially while performing resource-intensive tasks.
Trusted – Since .NET is backed by Microsoft – there is a good level of trust associated with it, especially on the security front. Microsoft takes security very seriously and releases patches as soon as new threats are discovered.
Support– There are a large number of .NET developers worldwide and a large number of libraries and packages are available for .NET. This makes it easy to solve our technical challenges very quickly. Being open-source, a large number of developers and companies support the .NET platform.
Limitations
So far we have discussed the major benefits of .NET. However, there are a few limitations as well:
Licensing costs– Even though .NET is open source, building apps are still expensive mostly due to licensing costs associated with Visual Studio and related Application Lifecycle Management(ALM) tools. On top of that, even though it works on Linux and Mac, the best platform for .NET development is still Windows which causes additional licensing costs.
Memory leaks– Developers frequently criticize .NET for memory leaks related issues. It has an inbuilt garbage collector to detect and solve these kinds of issues. However, many times developers have to spend additional effort to troubleshoot and fix these issues.
Limited Object-Relational support– .NET has its ORM system called the Entity Framework. However, It isn’t considered flexible enough to support all kinds of database designs.
Vendor lock-in – While some technologies like .NET Core(including .NET 5+), Xamarin, etc. are open sources, a major portion of the .NET ecosystem is still very much proprietary to Microsoft. This means that we might be locked with a specific vendor. Moreover, it will be difficult to switch to a different vendor in the future.
Unstable releases and limited documentation– Many times, new .NET versions were unstable during the initial phases. On top of that, it lacked proper documentation in many areas. This caused many difficulties for developers. Apart from that, the .NET to .NET Core transition was huge with many breaking changes and it was not feasible for many organizations to migrate their existing applications.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about .NET and its capabilities. Also, we looked at the different programming languages that .NET supports and the different types of applications that we can build using it. Additionally, we looked at the different tools that we can use for .NET development and the .NET developer community.